Data-Driven HR: Reducing Turnover
How HR Analytics Transformed Performance Management and Reduced Turnover
A department within the organization had been experiencing high turnover due to performance-related issues.
Effective performance management is the foundation of employee engagement and retention. When done well, it fosters growth, accountability, and alignment between employees and leadership. However, when it falls short, organizations experience higher turnover, declining morale, and unresolved performance gaps.
In this case study, I’ll share how I leveraged HR analytics and mixed-methods research to diagnose performance management challenges, uncover the root causes of turnover, and drive a 25% improvement in employee turnover and performance.
Challenges
- Lack of Clarity: Leadership struggled to define the specific issues within performance management
- Corporate Sensitivities: Performance discussions were delicate and required a diplomatic approach
- Limited Employee Feedback: Direct surveys weren’t an option, necessitating creative data collection methods
- Stakeholder Alignment: Research findings needed to balance leadership expectations with HR feasibility
Objectives
- Identify the root causes of performance management challenges and turnover
- Provide data-driven insights using workforce analytics and qualitative research
- Develop actionable recommendations that align with organizational culture and leadership priorities
Business Impact
- 25% improvement in employee turnover and performance ratings within six months.
- Enhanced managerial coaching programs based on findings.
- Stronger leadership awareness and commitment to addressing employee concerns.
- HR implemented a structured performance monitoring framework for long-term tracking.
- Follow-up measurement plan established to assess ongoing impact.
Problem Framing
The project began with consultative conversations with leadership to clarify challenges and objectives. Often, management lacks clear direction on how HR analytics can help, making these discussions crucial for refining the problem statement and aligning research with strategic priorities.
In this case, conversations with the department’s VP helped narrow the focus to performance management (PM) as the primary contributor to employee turnover. By translating leadership concerns into clear, research-driven questions, I ensured that the analysis would yield meaningful insights and practical solutions.
Actions Taken
- Engaged leadership to understand workforce challenges.
- Translated broad concerns into clear, actionable research questions.
- Identified performance management as a key driver of turnover
Refined
Research Questions
- What specific performance management challenges are driving high turnover?
- How can managers improve coaching and feedback?
- What HR interventions can support stronger performance management?
Aligning with
Leadership Prioritie
- Framed data-driven insights to resonate with leadership in a corporate environment.
- Ensured HR recommendations were practical, strategic, and business-aligned.
- Secured leadership buy-in, driving meaningful change.
Methodology
To diagnose performance management challenges, I combined data analysis with direct stakeholder collaboration, ensuring insights were informed by multiple perspectives. This approach allowed leadership to identify critical issues and implement measurable improvements in performance management.
By leveraging both quantitative workforce analytics and qualitative exit survey data, I developed a comprehensive understanding of departmental challenges. These insights narrowed the research focus toward performance management as a key driver of turnover.
With this foundation, the next step was to design targeted research strategies to validate these findings and develop actionable recommendations.
Exploratory Data Analysis
At this stage, I didn’t have a clear roadmap for the research. To gain a foundational understanding of the department’s challenges, I leveraged available data sources within a short time frame.
By analyzing internal documents, workforce metrics, and exit surveys, I refined the problem scope and identified key areas for deeper investigation.
Sources: Meeting notes, job postings, performance standards, recognition programs, and warning letters.
Analysis: Synthesized key themes to refine research questions.
Key Insights:
- Department background & expectations.
- Employee responsibilities & evaluation criteria.
- Recognition & incentive systems.
- Common performance challenges.
Sources: HR dashboards (turnover rates, promotions, performance ratings).
Analysis: Standardized metrics and addressed missing data.
Key Insights:
- Turnover Trends – Benchmarked department turnover against company-wide trends.
- Promotion Patterns – Assessed time-to-promotion and recognition discrepancies.
- Performance Metrics – Evaluated ratings by manager, location, and tenure
- Employee Clustering – Identified traits of low performers.
Sources: HR exit surveys, employee interviews.
Analysis: Coded and quantified qualitative feedback for trend analysis.
Key Insights:
- Thematic Analysis – Identified recurring employee frustrations.
- Workforce Correlation – Mapped qualitative feedback to workforce data to detect patterns.
Deep Dive
After analyzing workforce trends, I sought to capture manager and employee perspectives on the performance improvement process, their challenges, and how the organization could better support managers in driving employee performance.
To gain managerial insights, I identified key stakeholders and selected tailored engagement methods to ensure a holistic understanding of performance management challenges.
Stakeholder Mapping
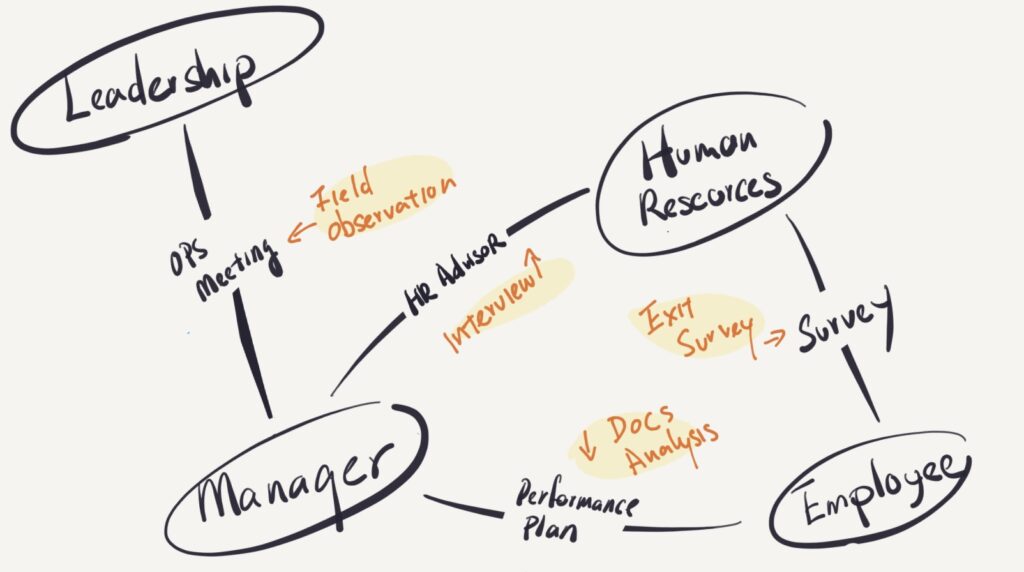
| Stakeholder | Method | Impact |
| Leadership (VPs & Directors) | One-on-one discussions | Refined research scope & aligned findings with business priorities. |
| HR Advisors | Structured focus groups | Identified managerial challenges in performance evaluations & employee development. |
| Frontline Managers | Field observations | Captured real-time discussions on performance issues. |
Overcoming Barriers to Collect Employee Feedback
Initially, I proposed conducting a survey to gather direct feedback from managers and employees. However, this approach was rejected due to:
- Sensitivity concerns – Employees might panic and misinterpret the survey’s intent.
- Approval complexity – Multiple layers of leadership approval would delay implementation.
- Company culture fit – Surveys may perceived as intrusive and misaligned with organizational norms.
Recognizing these challenges, I pivoted my approach by leveraging existing data sources (exit interviews) and engaging key stakeholders (leadership, HR, and frontline managers) to extract meaningful insights without disrupting established processes.
Manager Perspective:
Leadership & HR Advisor Discussions
To explore managerial pain points, I conducted structured meetings and focus groups to identify the challenges managers face in addressing performance issues and pinpoint gaps in the current evaluation framework.
Key Discussion Questions
- How do you assist managers? What stands out?
- What are the most common challenges and frustrations managers face?
- Can you share examples of employees who improved (or didn’t) after entering a performance improvement process?
- What recommendations do you have to improve performance management?


Manager Perspective:
Field Observations with Frontline Managers
Following discussions with leadership, I attended a quarterly zone review—a two-day event where directors and managers evaluate employee performance and discuss strategies for improvement.
This real-time exposure provided:
- Cross-functional collaboration insights – How leadership, HR, and managers interact in decision-making.
- A deeper understanding of managerial perspectives – What criteria they use to assess performance and what challenges they face.
- A window into organizational culture – How performance management norms are shaped at different levels.
Employee Perspectives:
Exit Survey Analysis
To overcome barriers to direct employee feedback, I leveraged exit interviews to capture employee sentiment on performance management.
Key questions included:
- Did your manager support your development? – Assessed the effectiveness of performance coaching.
- Why are you leaving? – Identified common themes contributing to turnover.
- What would you improve about your work environment? – Captured employee frustrations related to performance management.

Initial Findings
By quantifying qualitative feedback, I integrated employee sentiment data with workforce analytics (tenure, turnover, performance ratings) to uncover patterns and correlations . This approach translated employee feedback into data-driven, actionable recommendations for leadership, ensuring insights led to measurable improvements.
The qualitative insights reinforced workforce analytics, ensuring leadership understood both the business impact and human experience of performance management challenges.
- Managers struggled with performance coaching due to a lack of structured guidance.
- Employees felt unsupported in their development, leading to disengagement.
- Inconsistent evaluation standards created frustration among both managers and employees.
Presentation
Presenting the Voice: An Audience-Centered Approach
Data insights are only valuable if they lead to action. To drive meaningful change, I crafted a clear, engaging, and audience-centered presentation tailored for departmental directors and senior leadership.
Given the audience, my primary challenge was balancing transparency with diplomacy—ensuring the findings were not perceived as placing blame but rather as a constructive foundation for action.
Structuring the Presentation for Impact
I designed the presentation to guide leadership through a logical and compelling storytelling approach, ensuring they grasped both the data-driven findings 

 Setting the Stage
Setting the Stage
Establish urgency & leadership buy-in
Approach: Used workforce data 
 The Voice of Employees & Managers
The Voice of Employees & Managers
Humanize the data
Approach: Integrated exit survey feedback 

 Personalized Insights
Personalized Insights
Make the findings relatable
Approach: Used anonymous employee quotes 🏷️ to reinforce the emotional impact.
 Actionable Recommendations
Actionable Recommendations
Drive decision-making
Approach: Delivered practical, HR-backed solutions 
Making Data Digestible with Visuals
To ensure engagement and clarity, I incorporated compelling visuals that made complex workforce trends easy to understand:
- 📊 Trend Charts– Illustrated how turnover and performance issues evolved over time.
- 🔥 Heatmaps – Highlighted correlations between performance ratings and tenure.
- 💬 Word Clouds – Summarized common themes in employee feedback on Exit Surveys.
By combining data with storytelling, I ensured leadership not only understood the problem but also felt motivated to take action.
Impact
Leadership wasn’t surprised by the findings—managers had voiced similar concerns before. However, seeing these scattered insights consolidated into a structured, data-backed report created a sense of urgency that drove action.
By quantifying workforce trends and linking employee sentiment to turnover and performance declines, the research transformed abstract concerns into clear, actionable priorities.
In response, leadership launched targeted interventions to enhance:
- Managerial training to improve performance coaching.
- Employee support programs to foster development.
- Performance monitoring systems to track ongoing progress.
Six months later, a follow-up analysis revealed a 25% improvement in employee turnover and performance ratings—a direct outcome of data-driven decision-making.
This project translated insights into measurable change, establishing a framework for continuous improvement and long-term success.
Reflection
This project showcased my ability to incorporate business analytics, workforce data, and qualitative research to drive real organizational change.
By integrating workforce metrics, managerial feedback, and employee sentiment analysis, I helped leadership shift from gut-feel decision-making to a structured, data-driven approach, leading to sustained performance improvements.
Key Takeaways
- Data Storytelling is Key: Insights alone don’t drive action; how they are framed matters. Presenting workforce data as a structured narrative, linking it to real employee experiences, made leadership receptive and motivated to act.
- Stakeholder Alignment Drives Action: Successfully influencing leadership required navigating corporate sensitivities, ensuring the research was positioned as a tool for improvement, not blame.
- Blending Quantitative & Qualitative Data Creates Impact: Combining HR workforce analytics with exit survey sentiment analysis provided a holistic understanding of performance challenges, making recommendations more actionable.
Challenges & How I Overcame Them
- Data Limitations: Without direct employee surveys, I leveraged exit interviews as a proxy for employee sentiment, extracting meaningful insights from existing data.
- Cultural Barriers: Navigated corporate sensitivities by ensuring the research approach was non-disruptive, collaborative, and aligned with business priorities.
- Data Integration: Combined structured HR metrics with unstructured employee feedback, creating a cohesive, evidence-based narrative that leadership could act on.
Future Steps
- Long-Term Performance Monitoring: Establish an ongoing data tracking system to measure the sustained impact of interventions.
- Refining Managerial Training Programs: Use follow-up analysis to identify remaining gaps and tailor future leadership development programs.
Expanding Research Scope: Explore employee engagement surveys and behavioral analytics to gain even deeper workforce insights.